What Part Of The Brain Does Huntington's Disease Affect
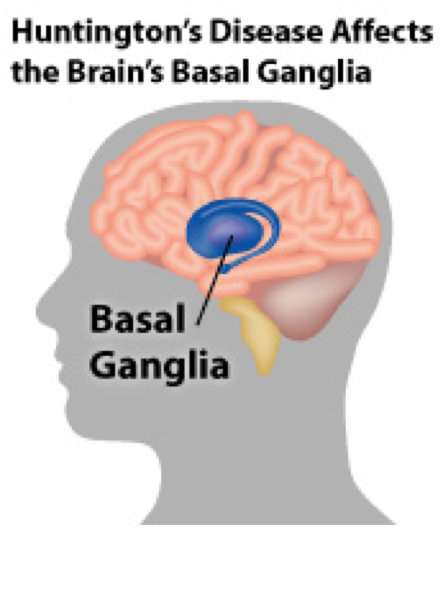
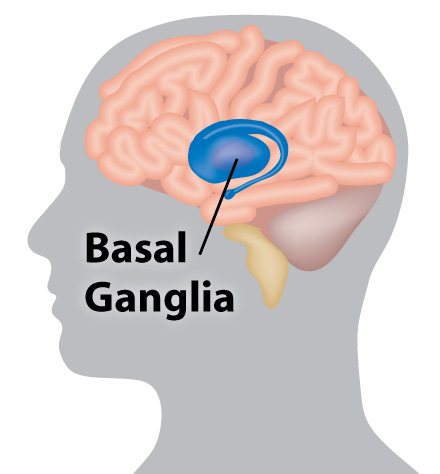
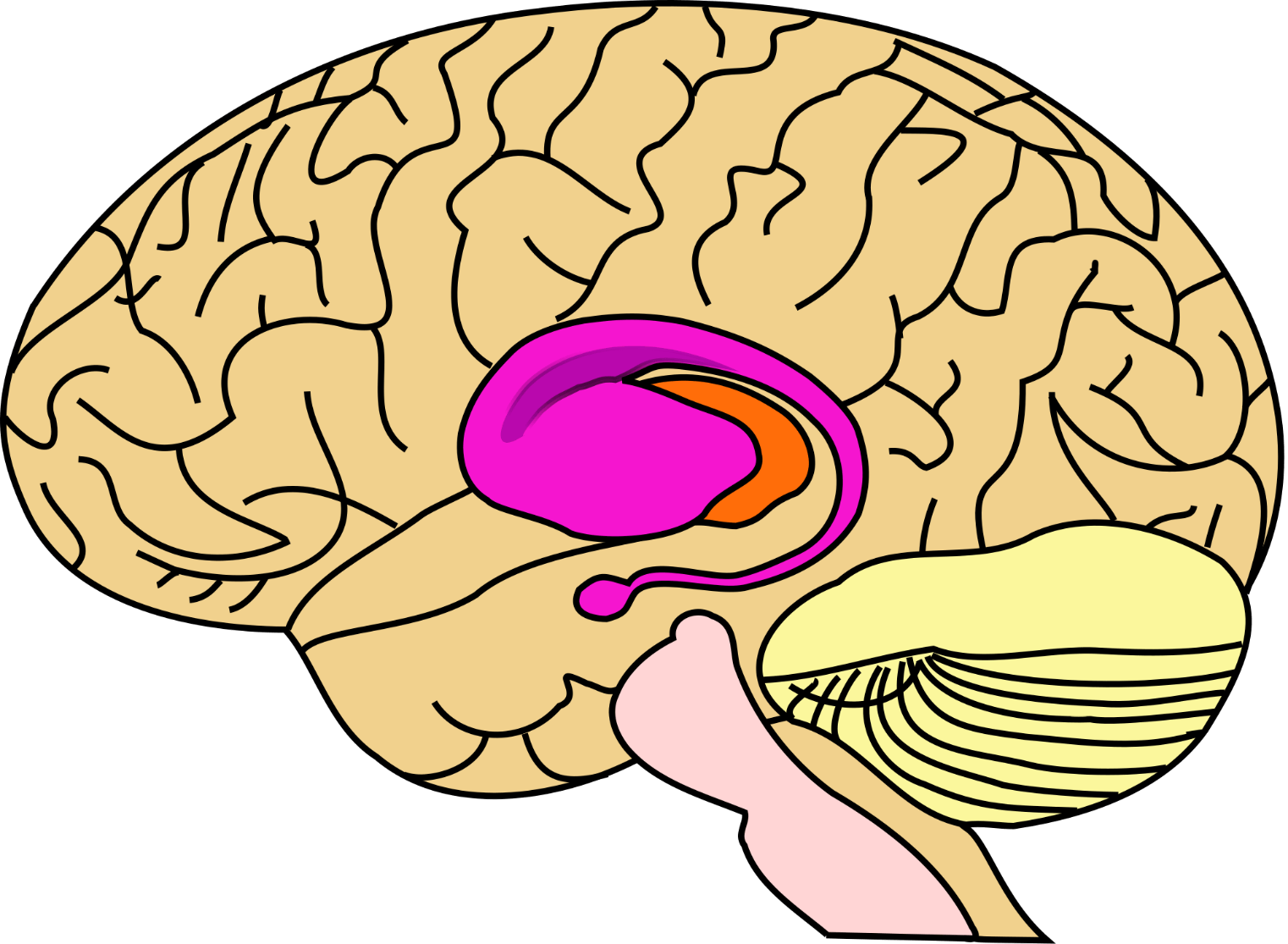
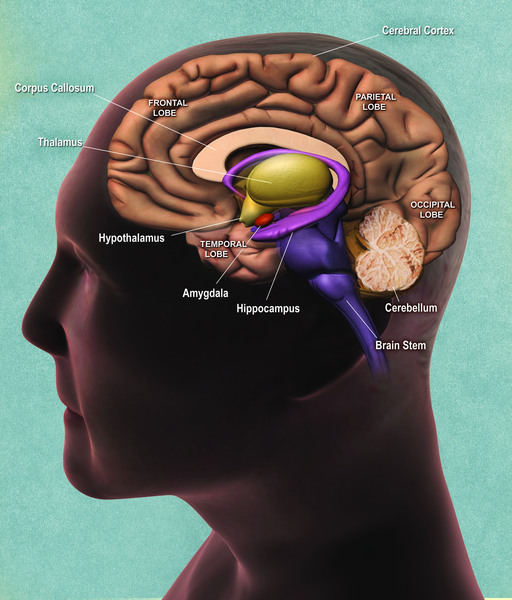
What part of the brain does huntington's disease affect. Pictured above in blue is the striatum an area deep in the brain that plays a key role in movement mood and behavior control. Hundingtons disease is a disease which destroys the part of the brain called the basal ganglia which is important for controlling. Adenosine A 2A receptors in the striatum play an important modulatory role of glutamatergic transmission to the GABAergic enkephalinergic neuron which function is particularly compromised in the early stages of Huntingtons disease S.
How Huntingtons affects your body. Huntingtons disease HD is a brain disease that is passed down in families from generation to generation. Huntingtons disease causes the deterioration and death of cells in certain areas of the brain.
It can interfere with movements of your body can affect your reasoning awareness thinking and judgement cognition and can lead to a change in your behaviour. What Is Huntingtons Disease. It is an inherited genetic condition that affects the brain and nervous system.
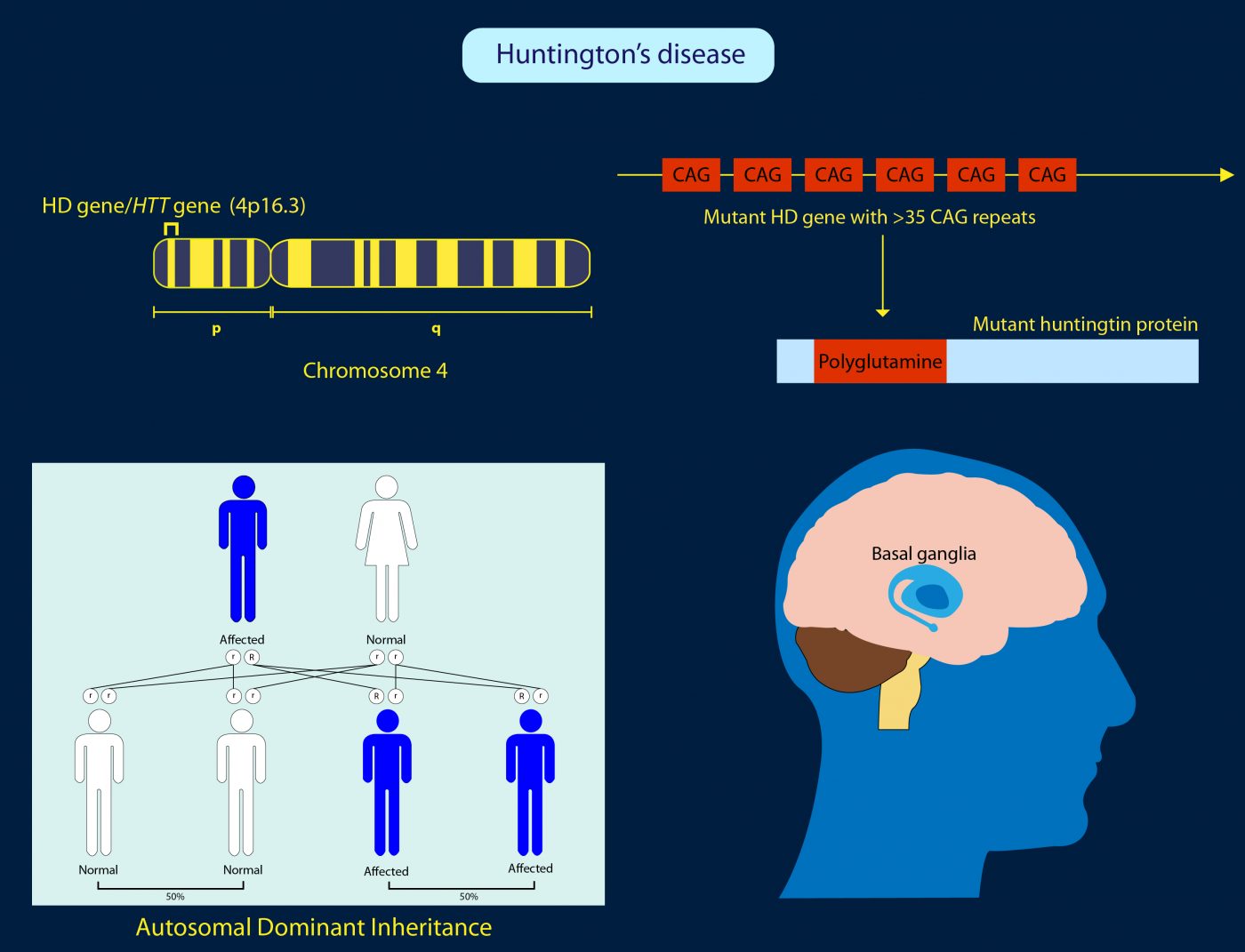
How does Huntingtons disease HD affect the brain. If you have a faulty version of the gene the protein it produces in fact damages these neurons instead of developing. In Huntingtons disease the mutant protein known as huntingtin leads to the degeneration of a part of the brain known as the basal ganglia causing the motor disturbances that represent one of.
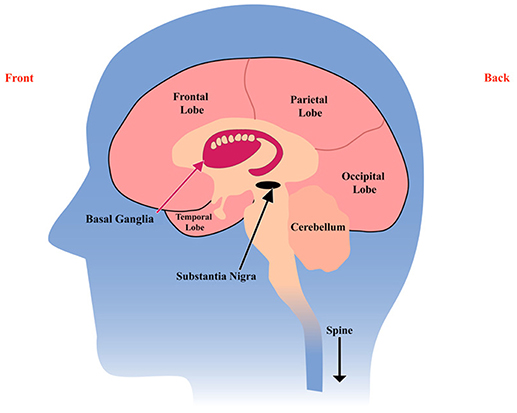
Huntingtons disease HD is named after George Huntington who first described it in 1872. The disease also impacts the brains cortex surface of the brain. Huntingtons Disease HD an inherited neurodegenerative disorder damages specific areas of the brain resulting in movement difficulties as well as cognitive and behavioral changes.
If you have Huntingtons it means you have a faulty version of the gene responsible for producing a protein that helps nerve cells neurons in certain parts of the brain to develop before birth. Because each area is linked to one or a handful of behaviors damage to an area leads to changes in the behavior it governs. The death of brain cells in certain areas of the brain results in a gradual loss of cognitive thinking physical and emotional function.
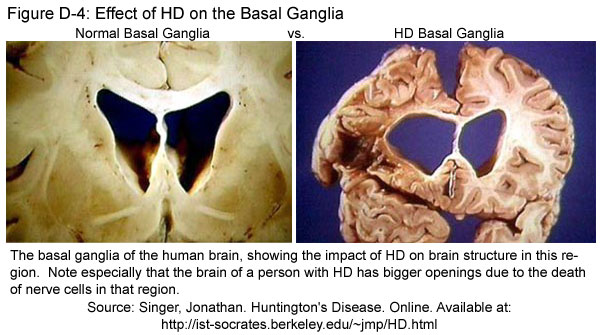
Huntingtons disease develops when misshapen proteins destroy neurons brain cells. The basal ganglia are collections of nerve cells located at the base of the cerebrum deep within the brain.
How Huntingtons affects your body.
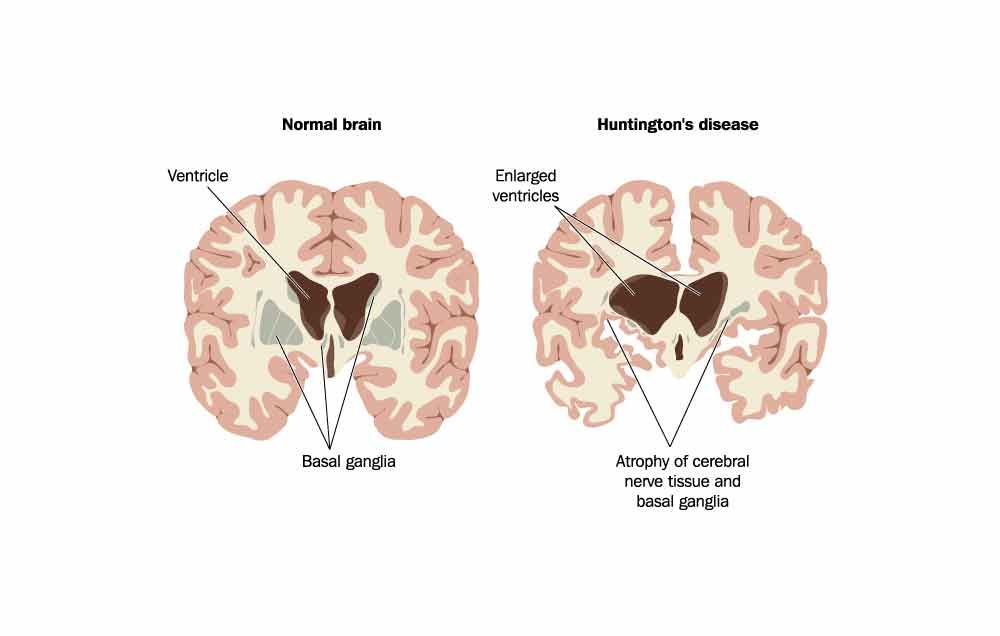
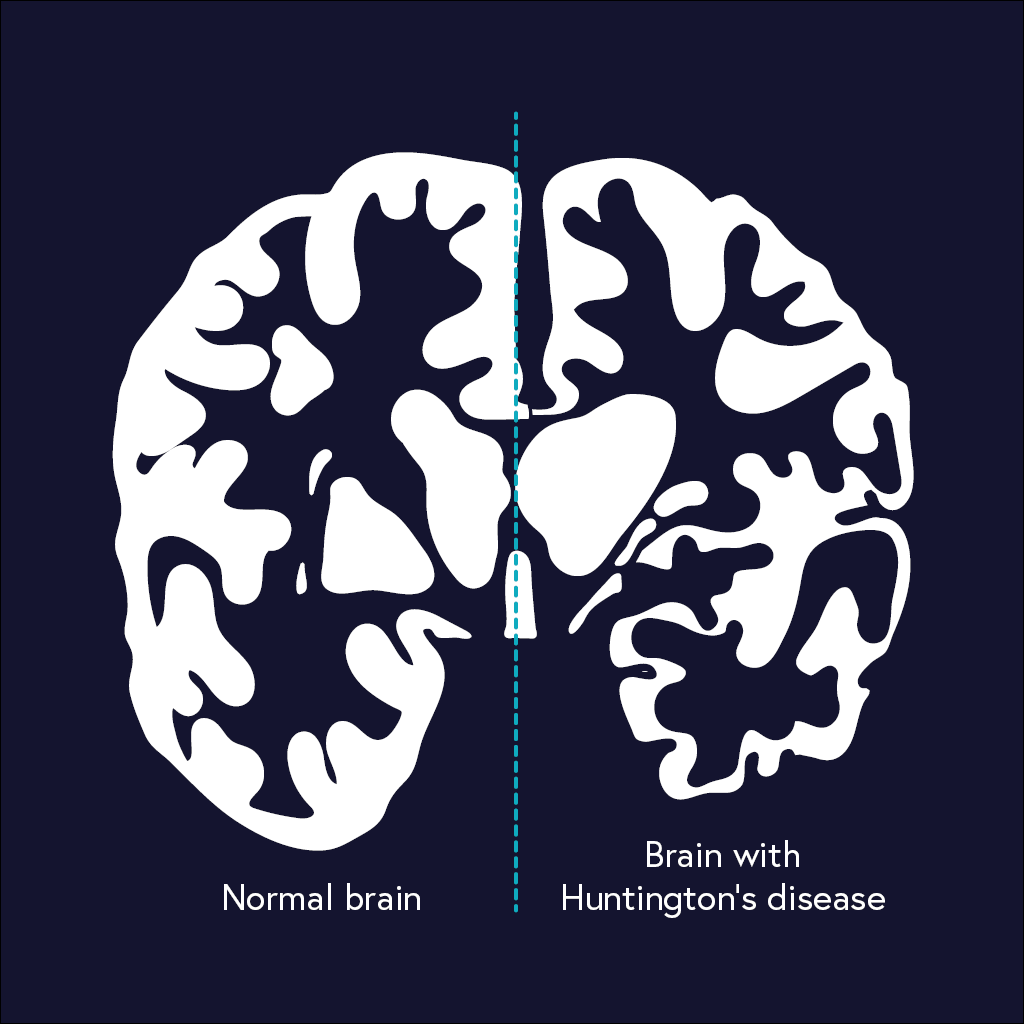
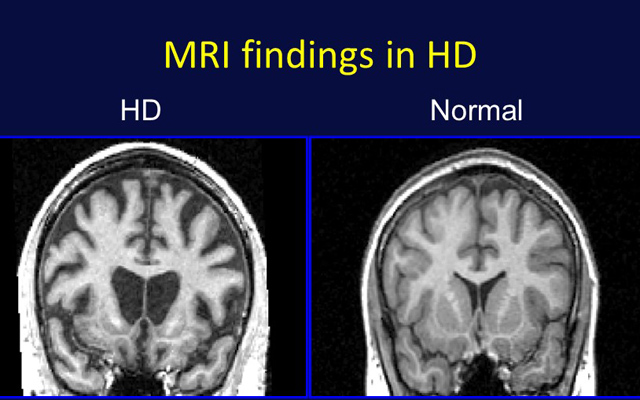
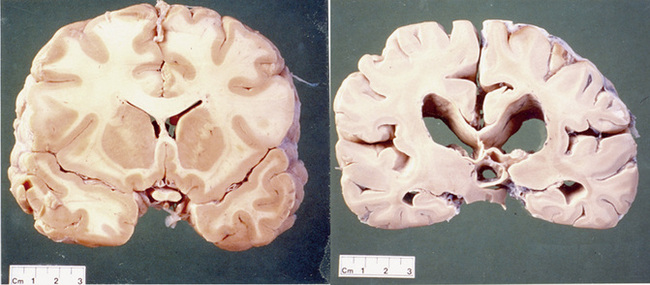
In Huntingtons disease the mutant protein known as huntingtin leads to the degeneration of a part of the brain known as the basal ganglia causing the motor disturbances that represent one of. Huntingtons Disease HD an inherited neurodegenerative disorder damages specific areas of the brain resulting in movement difficulties as well as cognitive and behavioral changes. Hundingtons disease is a disease which destroys the part of the brain called the basal ganglia which is important for controlling. Huntington disease is caused by gradual degeneration of parts of the basal ganglia called the caudate nucleus and putamen. Because each area is linked to one or a handful of behaviors damage to an area leads to changes in the behavior it governs. Huntingtons disease also known as Huntington disease is a neurological nervous system condition caused by the inheritance of an altered gene. Huntingtons disease is a complex and severely. Huntingtons disease is a genetic disorder affecting the central nervous system and which causes the progressive degeneration of brain cells. The part of the brain that selectively degenerates in people with Huntingtons disease HD called the striatum is almost entirely destroyed in the late stages of the disease.
This leads to the degeneration of motor skills and cognitive abilities as well as behavioral difficulties. The basal ganglia are collections of nerve cells located at the base of the cerebrum deep within the brain. It is an inherited genetic condition that affects the brain and nervous system. How Huntingtons affects your body. The disease also impacts the brains cortex surface of the brain. Pictured above in blue is the striatum an area deep in the brain that plays a key role in movement mood and behavior control. How does the disease affect the brain.























Post a Comment for "What Part Of The Brain Does Huntington's Disease Affect"