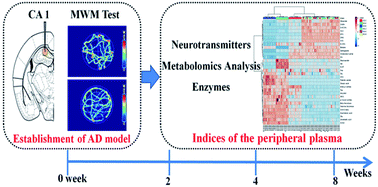
Neurotransmitters Associated With Alzheimer's Disease
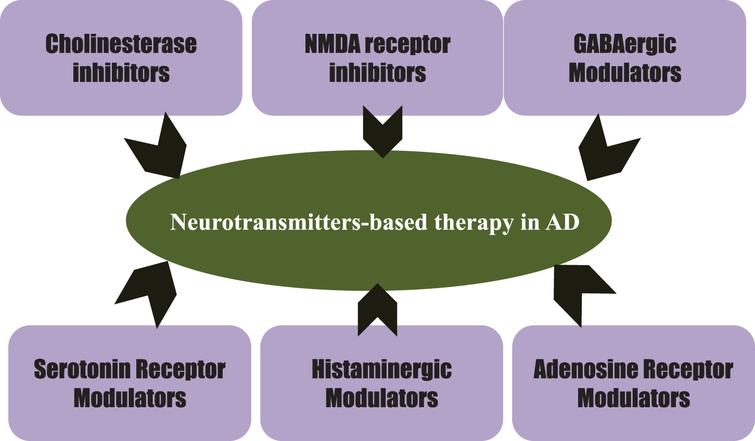
Neurotransmitters associated with alzheimer's disease. In the brains of Alzheimers victims a number of different kinds of damage can occur within brain cells. Acetylcholine ACh a neurotransmitter essential for processing memory and learning is decreased in both concentration and function in patients with Alzheimers disease. The purpose of this mini-forum Neurotransmitters and Alzheimers Disease is to critically assess the current status of neurotransmitters in Alzheimers disease.
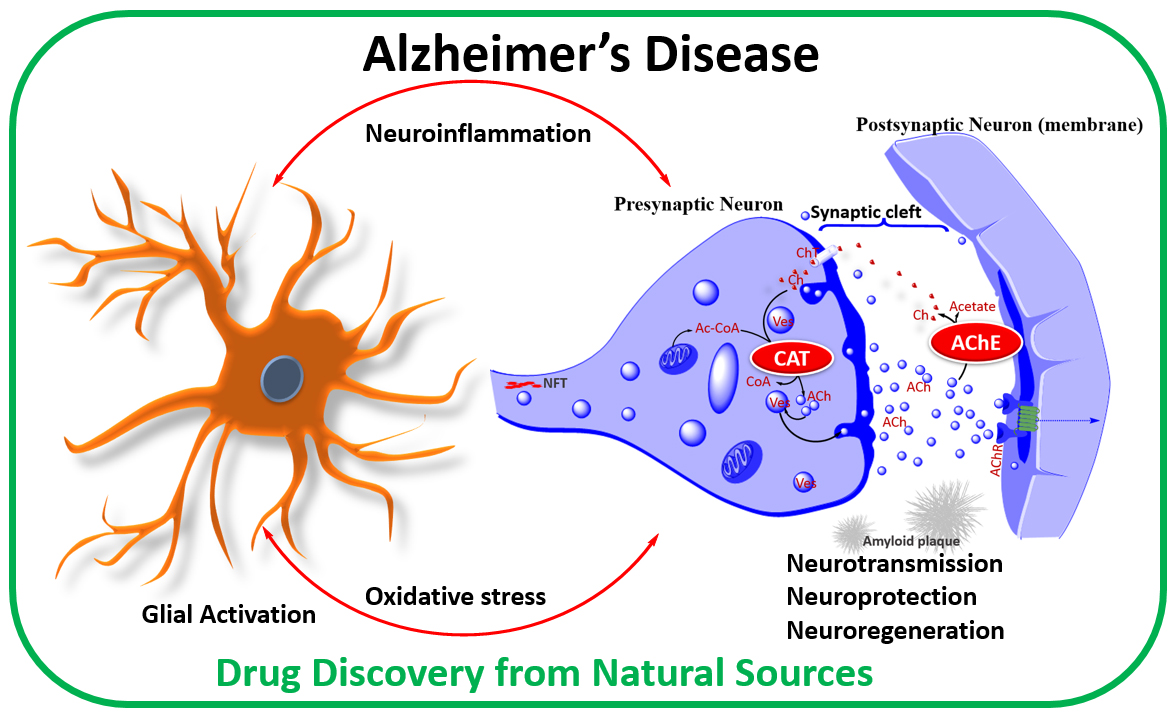
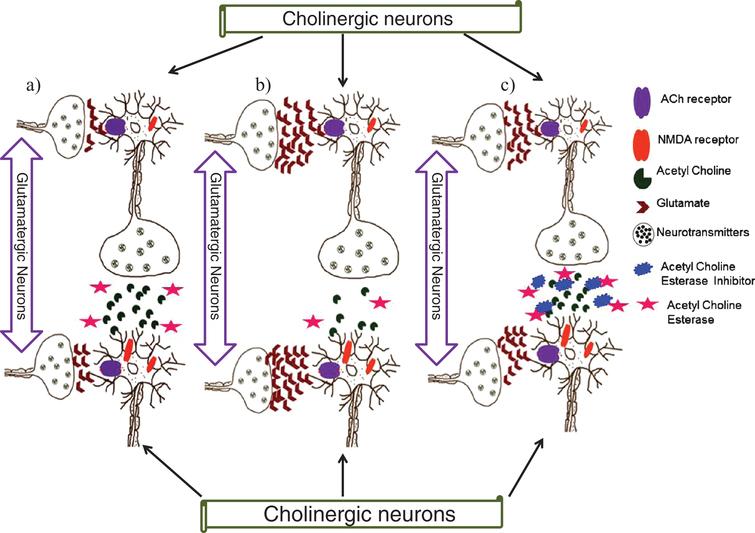
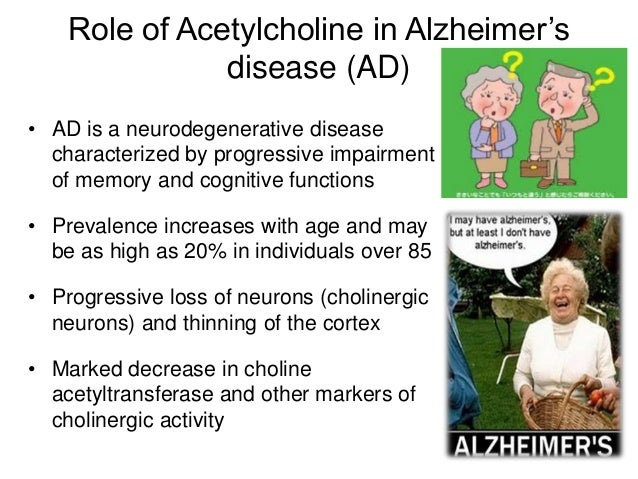
Acetylcholine is one such neurotransmitter the deficiency of which is hypothesized to be one of the factors responsible for the intellectual deterioration seen in both Alzheimers disease and in normal ageing 6. Evidence exists for both cholinergic and glutamatergic involvement in the etiology of Alzheimers disease. Acetylcholine ACh a neurotransmitter essential for processing memory and learning is decreased in both concentration and function in patients with Alzheimers disease.
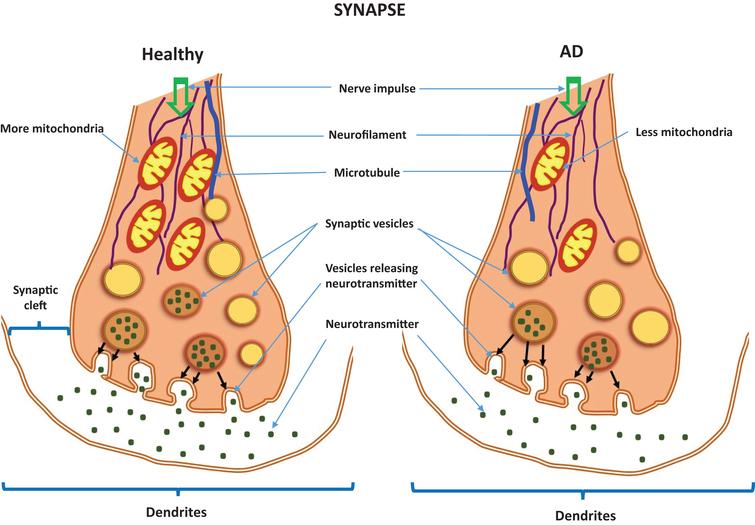
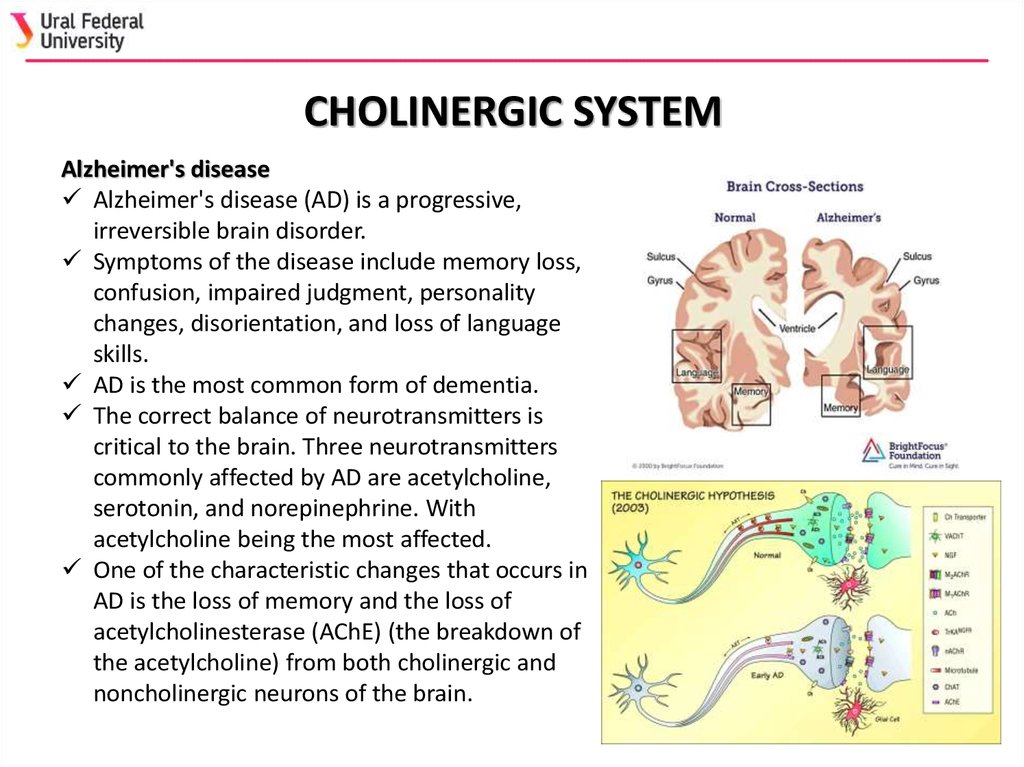
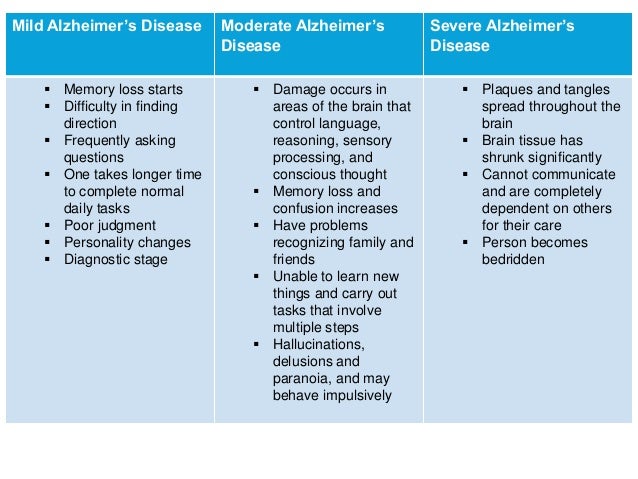
At first Alzheimers disease typically destroys neurons and their connections in parts of the brain involved in memory including the entorhinal cortex and hippocampus. Acetylcholine is essential in learning and memory. Individuals with AD have low levels of ACh.
In 15 patients with Alzheimers disease and in 10 with Downs syndrome at middle age there was severe atrophy neurofibrillary degeneration and loss of pigmented dopaminergic nerve cells from ventral tegmental area A10 whereas nerve cells in neighbouring substantia nigra A9 were much less affected in all three respects. Two neurotransmitters seem to play a role in Alzheimers Disease. Acetylcholine ACh activates muscles and helps with arousal short-term memory and learning.
Thus it is well established that the nucleus basalis of Meynert and related areas of the basal forebrain show a distinct loss of cholinergic cell bodies in patients with Alzheimers disease. Alzheimers disease is characterized by markedly reduced concentration of acetylcholine in hippocampus and neocortex caused by degeneration of cholinergic neurons. Yoga and Neurotransmitters Yogasana practice is known to release all these good neurotransmitters particularly the serotonin dopamine and norepinephrine and keep them in a good balance.
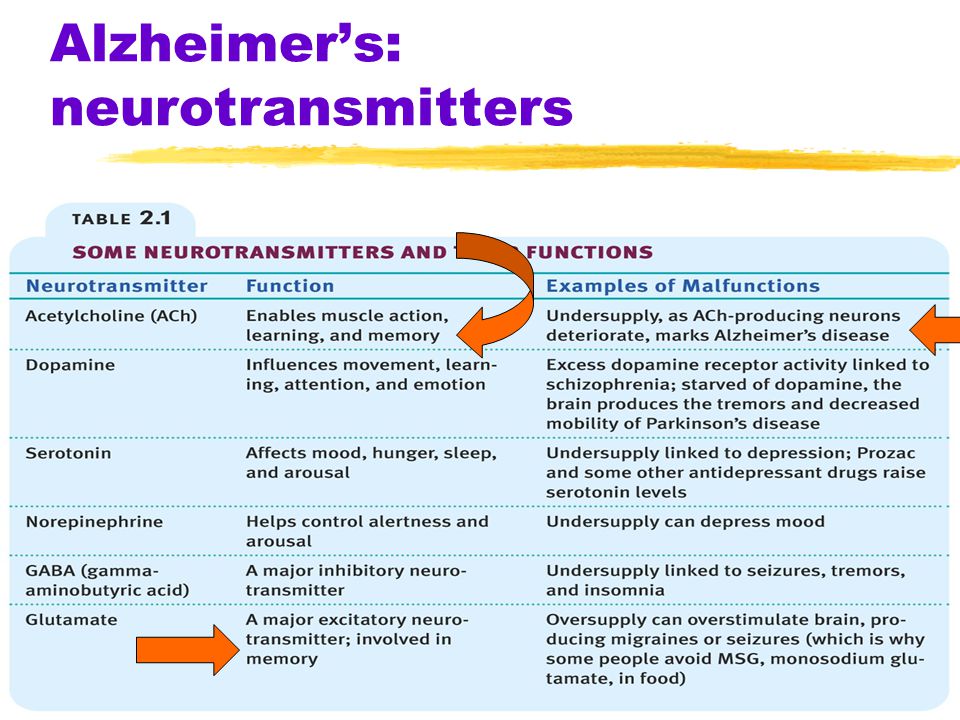
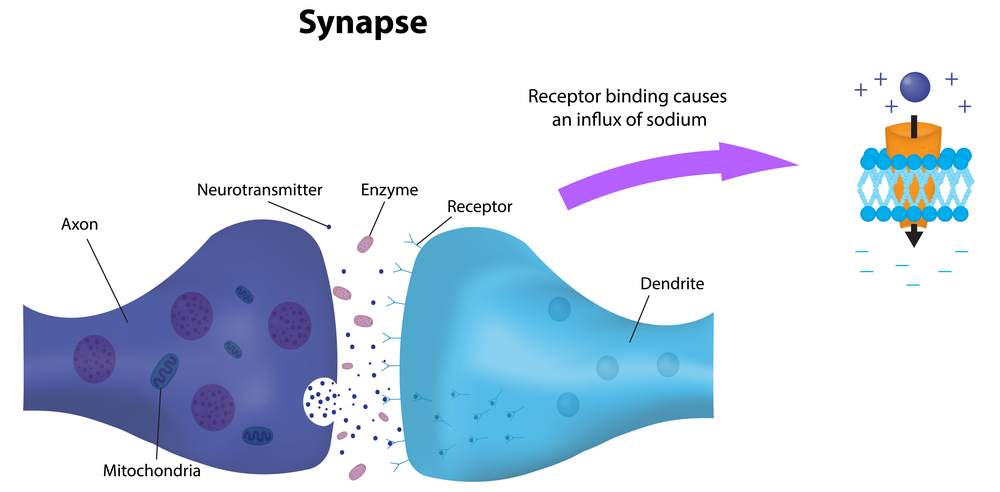
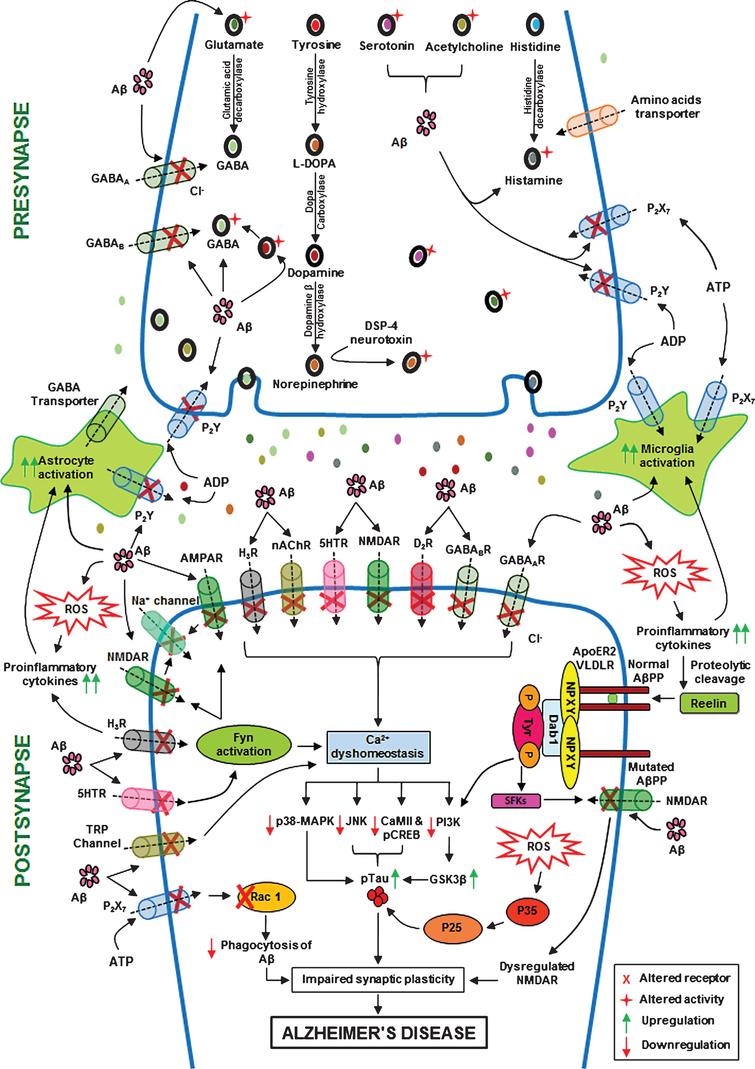
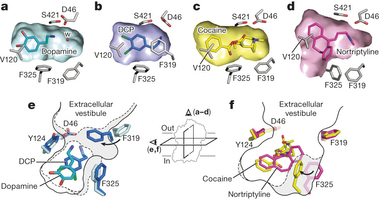
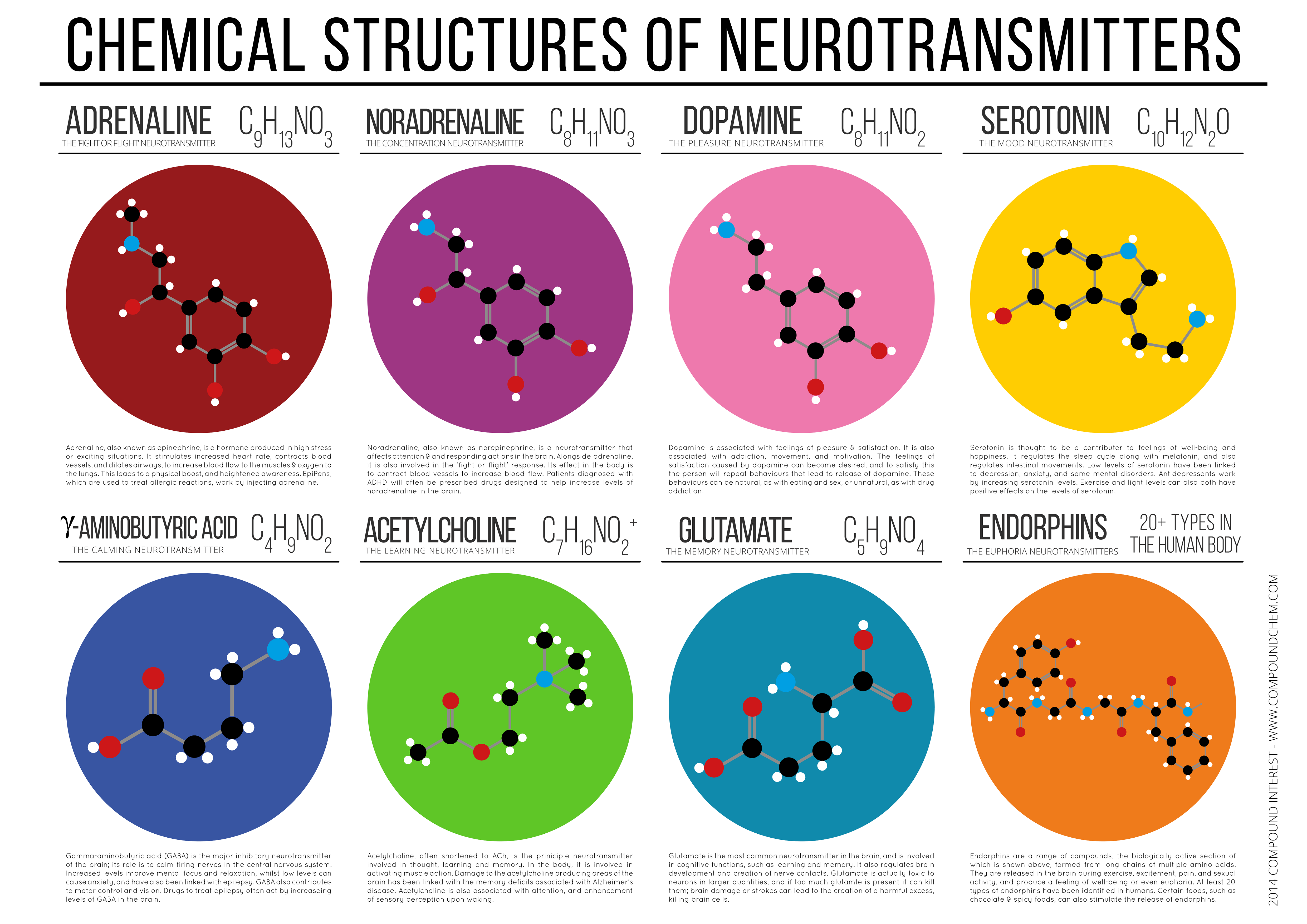
Some common neurotransmitters are acetylcholine norepinephrine dopamine serotonin and gamma aminobutyric acid GABA. Neurotransmitters are essential neurochemicals that maintain synaptic and cognitive functions in mammals including humans by sending signals across pre- to post-synaptic neurons. In the cases of both Alzheimers and vascular dementia the neurotransmitters serotonin norepinephrine and acetylcholine in particular are dangerously reduced.
The main disorders associated with Ach are Alzheimers disease and Myasthenia gravis. Acetylcholine ACh activates muscles and helps with arousal short-term memory and learning.
Acetylcholine ACh a neurotransmitter essential for processing memory and learning is decreased in both concentration and function in patients with Alzheimers disease.
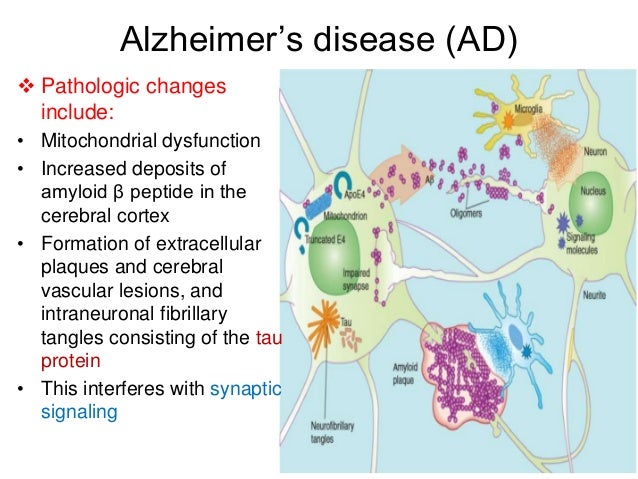
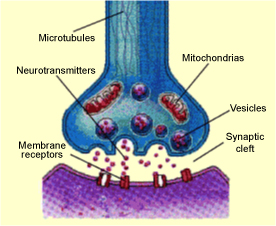
In 15 patients with Alzheimers disease and in 10 with Downs syndrome at middle age there was severe atrophy neurofibrillary degeneration and loss of pigmented dopaminergic nerve cells from ventral tegmental area A10 whereas nerve cells in neighbouring substantia nigra A9 were much less affected in all three respects. Acetylcholine is one such neurotransmitter the deficiency of which is hypothesized to be one of the factors responsible for the intellectual deterioration seen in both Alzheimers disease and in normal ageing 6. There has been considerable interest in the involvement of the major neurotransmitters in the possible aetiology of Alzheimers disease. Neurofibrillary tangles are bits of protein clogging neurons. In the cases of both Alzheimers and vascular dementia the neurotransmitters serotonin norepinephrine and acetylcholine in particular are dangerously reduced. The best known neuromodulators are also neurotransmitters such as dopamine serotonin acetylcholine histamine and norepinephrine. Acetylcholine ACh activates muscles and helps with arousal short-term memory and learning. Nerve cells send out neurotransmitters to activate or inhibit neighbouring nerve cells speeding up or slowing down nerve functions such as muscle coordination behavior mood blood flow body temperature and pain. Acetylcholine ACh a neurotransmitter essential for processing memory and learning is decreased in both concentration and function in patients with Alzheimers disease.
It later affects areas in the cerebral cortex responsible for language reasoning and social behavior. In 15 patients with Alzheimers disease and in 10 with Downs syndrome at middle age there was severe atrophy neurofibrillary degeneration and loss of pigmented dopaminergic nerve cells from ventral tegmental area A10 whereas nerve cells in neighbouring substantia nigra A9 were much less affected in all three respects. This deficit and other presynaptic cholinergic deficits including loss of cholinergic neurons and decreased acetylcholinesterase activity underscore the cholinergic hypothesis of Alzheimers disease. The main disorders associated with Ach are Alzheimers disease and Myasthenia gravis. This deficit and other presynaptic cholinergic deficits including loss. Evidence exists for both cholinergic and glutamatergic involvement in the etiology of Alzheimers disease. A neurotransmitter that enables learning and memory and also triggers muscle contraction low levels of this is linked to Alzheimers disease botox and Black Widow venom affects this neurotransmitter.
































Post a Comment for "Neurotransmitters Associated With Alzheimer's Disease"