Treatment Of Neurogenic Shock
Treatment of neurogenic shock. The practical treatment of these patients rests on initially restoring intravascular volume and if symptoms of neurogenic shock persist vasopressors such as dopamine should be used. The aim of treatment in neurogenic shock is stabilizing the patient and preventing irreversible tissue damage. They replenish fluid levels in the veins to help.
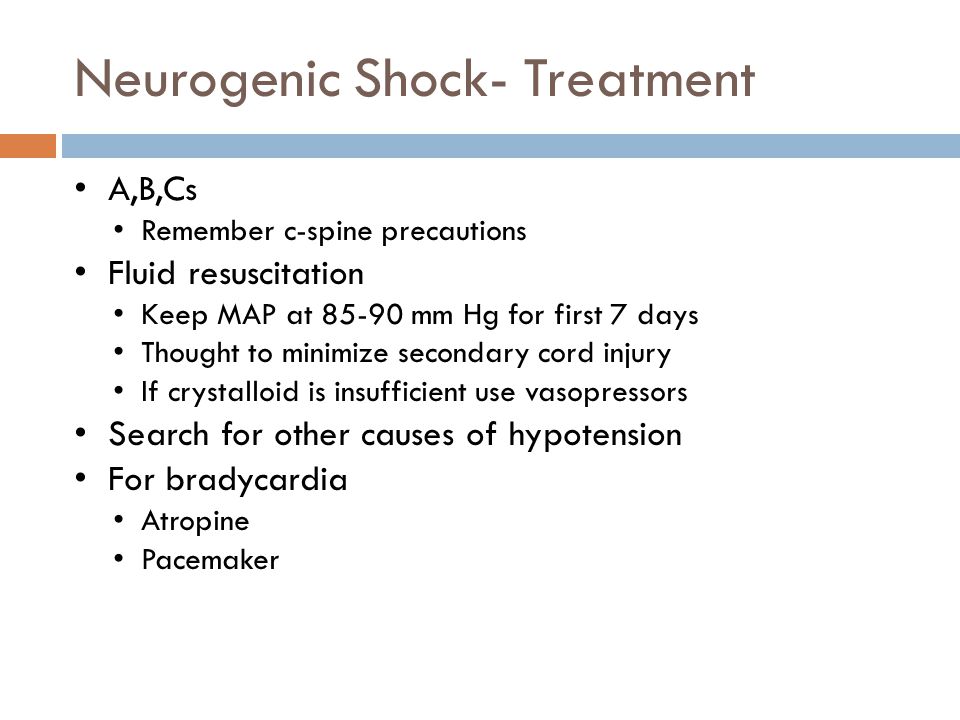
Judicious fluid replacement with isotonic crystalloid solution to a maximum of 2 L is the initial treatment of choice. The goal of treatment in the first week after sustaining an SCI is to maintain a mean arterial blood pressure of 85 mm Hg. Hypotension should be treated first to prevent secondary injury.
Some institutions would utilize the use of pressor agents to maintain hemodynamic stability of the body. Advertisement The patient is examined carefully and hisher general condition is assessed thoroughly. The Trauma Audit and Research Network database for an adult major trauma centre was used to isolate patients with a spinal cord injury.
If a spine injury causes neurogenic shock stabilizing the spine is often the first step in treatment. A massive transfusion protocol MTP should be in place for any hospital that manages trauma Pathophysiology and classification of shock in childrenclinically indistinguishable reactions. The first-line treatment for hypotension is intravenous fluid resuscitation.
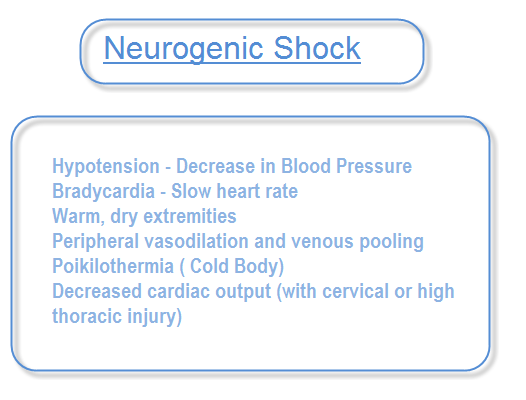
In the case of isolated neurogenic shock the resultant vasodilation results in pooling of blood and decreased venous return to the heart. Specific treatment of neurogenic shock at the accident scene after decreasing peripheral pooling by positioning andor the use of a shock suit should include the administration of 04 mg of atropine intravenously to help block the dominant vagal effect ie bradycardia. This is to allow appropriate.
The use of dopamine Intropin. Initial management of neurogenic shock is focused on hemodynamic stabilization. MAP at 60 to 70 mm Hg or a systolic pressure at 80 to 90 mmHg.
Neurogenic shock nursing NCLEX review of the treatment nursing interventions pathophysiology and signs and symptomsNeurogenic shock is a form of distribu. The primary management for neurogenic shock involves the administration of vasopressors and inotropic agents.
Vasopressors will increase peripheral vascular resistance and inotropic agents will increase heart rate.
These changes will result in a more evenly distributed blood volume within the circulatory system. If a spine injury causes neurogenic shock stabilizing the spine is often the first step in treatment. Neurogenic Shock Treatment IV Fluids. The goal of treatment in the first week after sustaining an SCI is to maintain a mean arterial blood pressure of 85 mm Hg. The first-line treatment for hypotension is intravenous fluid resuscitation. The use of dopamine Intropin. Hypotension should be treated first to prevent secondary injury. Advertisement The patient is examined carefully and hisher general condition is assessed thoroughly. These changes will result in a more evenly distributed blood volume within the circulatory system.
The practical treatment of these patients rests on initially restoring intravascular volume and if symptoms of neurogenic shock persist vasopressors such as dopamine should be used. The primary management for neurogenic shock involves the administration of vasopressors and inotropic agents. These changes will result in a more evenly distributed blood volume within the circulatory system. Treatment for Neurogenic Shock. The aim of treatment in neurogenic shock is stabilizing the patient and preventing irreversible tissue damage. Judicious fluid replacement with isotonic crystalloid solution to a maximum of 2 L is the initial treatment of choice. This is to allow appropriate.




































Post a Comment for "Treatment Of Neurogenic Shock"